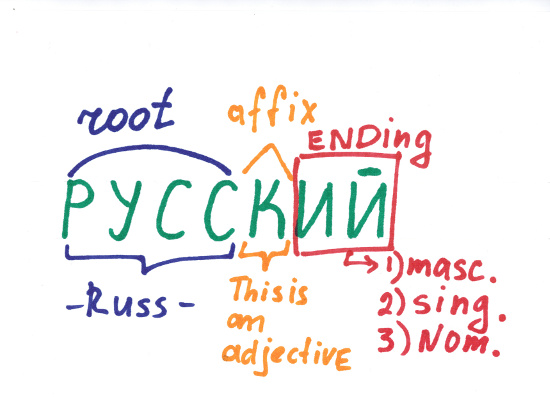
Russian grammar employs an Indo-European inflexional structure, with considerable adaptation.. Russian has a highly inflexional morphology, particularly in nominals (nouns, pronouns, adjectives and numerals).
Introduction. Nominative, called mianownik in the Polish language, is the first of the seven Polish cases. It describes people, objects and facts, and answers to the questions
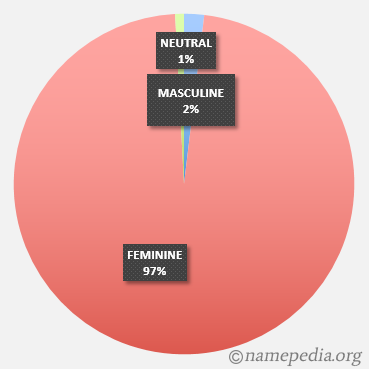

Nouns in Russian are divided into three genders: masculine, feminine and neuter. How to determine the gender in Russian? Look at the word’s ending
Gender and the Russian Case System. Russian Lesson 6. An introduction to Russian nouns. Learn how to determine the gender of a Russian noun and how to form the Nominative and Accusative case in Russian.
The Genitive Case – (Possession) The primary use of the Russian genitive case is to show possession. In English we often indicate this …
May 01, 2018 · Това е съвсем друга тема. ― Tova e sǎvsem druga tema. ― That’s quite a different matter.

Just to make things more complicated, certain masculine nouns are “weak” and take an “n” ending in all cases except the nominative. For example, most of the words for “man” in German (Junge, Bursche, Knabe, Bube) fall into this group:
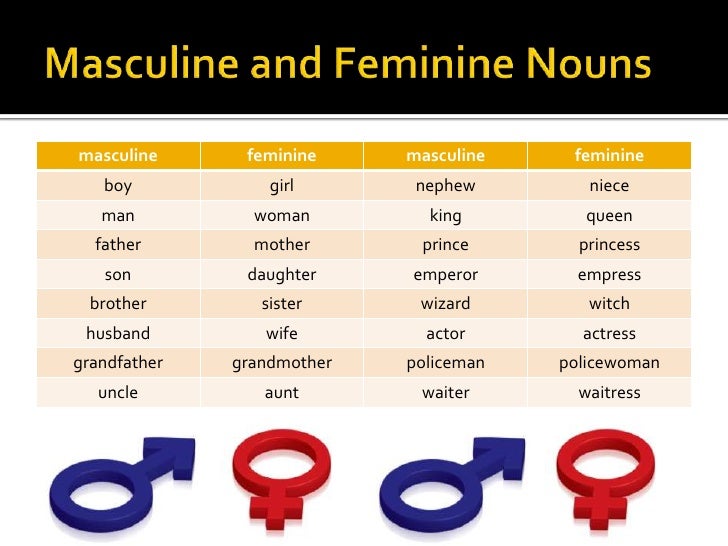

Russian nouns, adjectives and pronouns have genders: masculine; feminine; neuter; In English nouns have no gender, so this can be a confusing concept.
Lesson comments. Russian nouns can be either singular or plural. You know that to form a plural in English you need to add –s to the singular form.
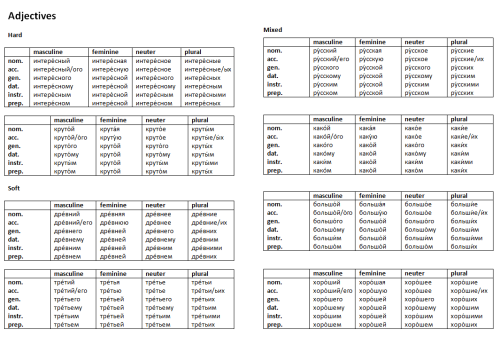
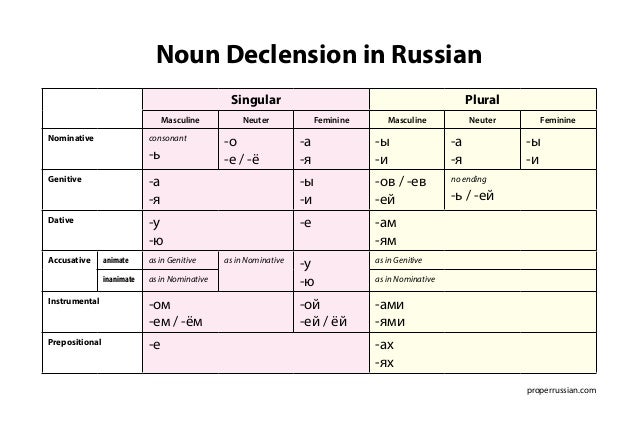
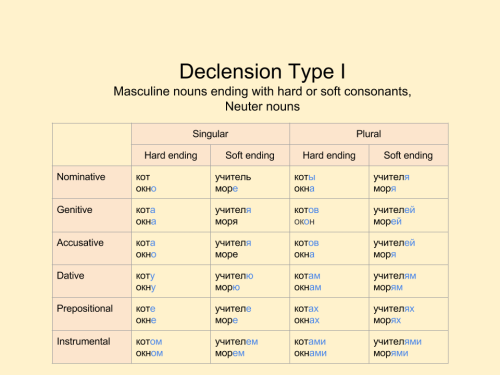
Explanation of the table: Add -а to masculine nouns ending in a hard consonant (брат) and neuter nouns ending in -o (окно).. Add -я to masculine nouns ending in -й, -ь (чай, учитель) and neuter nouns ending in -е, -ие (море, орудие).